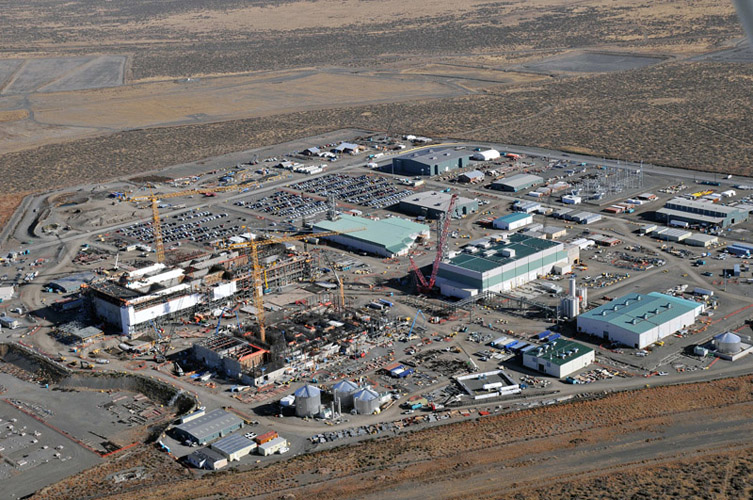
Hanford’s Waste Treatment and Immobilization Plant. (Photo: DOE)
The Department of Energy is asking for feedback on a new report analyzing potential options for preparing high-level radioactive waste for vitrification at the department’s Hanford Site near Richland, Wash. Vitrification is the process of treating radioactive waste by immobilizing it in glass.
The report, Waste Treatment and Immobilization Plant High-Level Waste Treatment: Analysis of Alternatives, was commissioned in response to a 2018 determination by the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers that it was unlikely the DOE would meet its mandated deadlines for treating Hanford’s tank waste.
The Integrated Waste Treatment Unit at the Idaho National Laboratory Site. (Photo: DOE)
The Department of Energy’s Office of Environmental Management (EM) said that the Integrated Waste Treatment Unit (IWTU), the radioactive liquid waste treatment facility at the Idaho National Laboratory Site, began its final heat-up in December prior to initiating radiological operations, planned for early this year.
IWTU crews were to follow a prescribed incremental process as the facility transitions from simulant to sodium-bearing waste (SBW), according to EM.
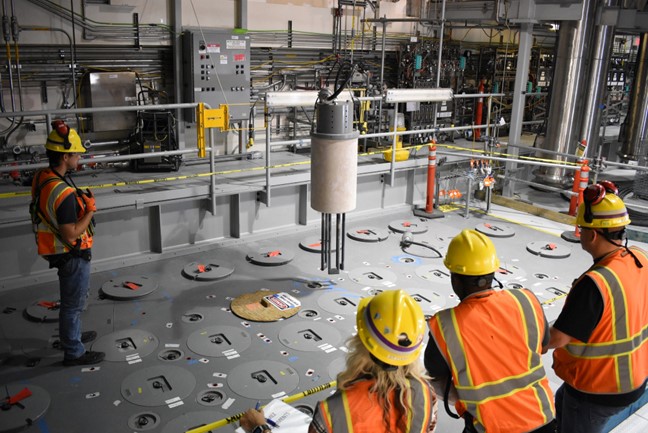
Workers walk down a passageway in Panel 8 at the Waste Isolation Pilot Plant in November. (Photo: DOE)
Employees have begun emplacing defense-related transuranic (TRU) waste in Panel 8 of the Waste Isolation Pilot Plant (WIPP) in New Mexico, the Department of Energy’s Office of Environmental Management (EM) announced in November. TRU waste is permanently disposed of at WIPP in rooms mined in a Permian salt bed 2,150 feet below the surface.
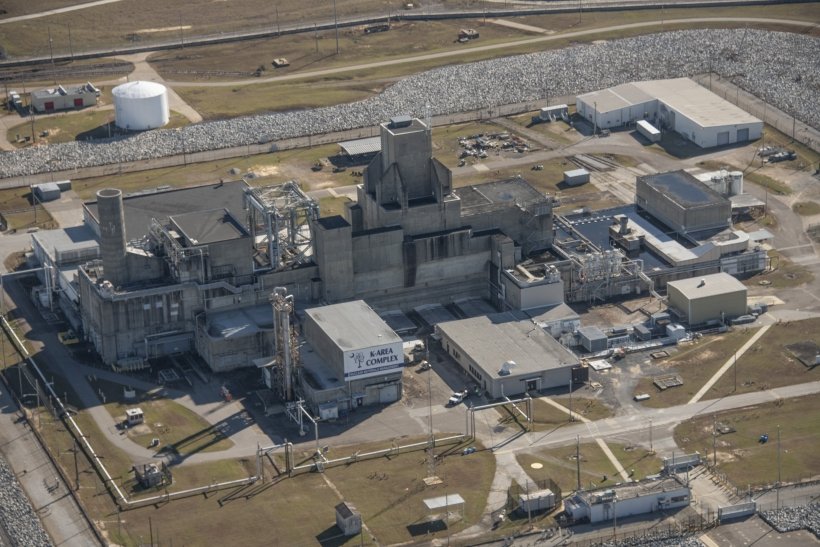
A view of Savannah River’s K Area, where employees began downblending plutonium in 2016. (Photo: DOE)
Contractor employees at the Department of Energy’s Savannah River Site in South Carolina recently exceeded their plutonium downblending goal for 2022 ahead of schedule as part of the ongoing activities to remove Pu from the state, the DOE’s Office of Environmental Management (EM) announced.
Workers install one of 18 startup heaters into Melter 1 of Hanford’s Low-Activity Waste Facility. (Photo: Bechtel National)
Heating of the first waste vitrification melter at the Department of Energy’s Hanford Site was paused after operators identified an “abnormal condition with the startup heater power supplies,” the DOE’s Office of River Protection (ORP) said. Heat-up of the 300-ton melter, which will be used to vitrify Hanford’s low-level radioactive tank waste, was initiated on October 8.
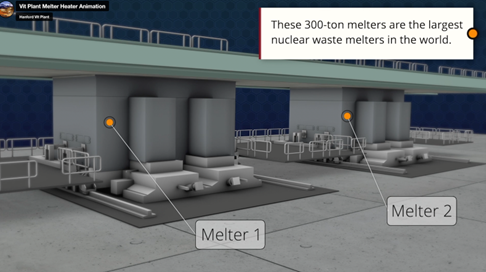
A screenshot from a 3D animation showing the heat-up of Hanford’s melters. (Image: DOE)
Crews at the Department of Energy’s Hanford Site, near Richland, Wash., have begun heating up the first of two 300-ton melters that will be used to vitrify mixed low-level radioactive and chemical tank waste. According to the DOE’s Office of Environmental Management (EM), initiating and completing the heating of the melter is a critical step to commissioning Hanford’s Waste Treatment and Immobilization Plant (WTP), which will treat and stabilize the site’s 56 million gallons of tank waste by immobilizing it in glass through the vitrification process.
Demolition of the MPPB, one of the last remaining major facilities at WVDP, is expected to be completed in about 30 months. (Photo: DOE)
The Department of Energy’s Office of Environmental Management (EM) said it has met one of its cleanup priorities for 2022 by beginning demolition of the Main Plant Process Building (MPPB) at the West Valley Demonstration Project (WVDP) in New York. Located 35 miles south of Buffalo, the 150-acre WVDP site is home to the only commercial spent nuclear fuel reprocessing facility to operate in the United States.
The Effluent Management Facility, part of the Waste Treatment and Immobilization Plant at the Hanford Site. (Photo: Bechtel National)
This spring, the U.S. Government Accountability Office (GAO) released an insightful report reviewing and summarizing the status and performance of the largest projects and operations within the Department of Energy’s Office of Environmental Management (EM), which is responsible for the cleanup of hazardous and radioactive waste at sites and facilities that have been contaminated from decades of nuclear weapons production and nuclear energy research.
Spain’s nuclear power plants are to use Holtec’s HI-STORM spent fuel storage technology. (Image: Holtec)
Holtec International announced that its flagship HI-STORM Multi-Purpose Canister (MPC) spent fuel storage technology was selected by Spain’s national company Enresa for a fleet of six nuclear power reactors at four plant sites in the country. Equipos Nucleares S.A. (ENSA), a Cantabria-based manufacturer of equipment for the Spanish nuclear fleet, was named a consortium partner with Holtec in the order, which was conducted under European Union procurement rules.












 The Department of Energy’s Office of Environmental Management (EM) released its
The Department of Energy’s Office of Environmental Management (EM) released its 
